  |
|
|
Customer Support | Products | Company Info | Links | Helpdesk |
|
|
||||
| Home | |
| Keylogger | |
| Reviews | |
| Demonstration | |
| Testimonials | |
| Photos | |
| Specifications | |
| FAQ | |
| Press releases | |
| Download | |
| Legal Disclaimer | |
| Affiliates | |
| Distributors | |
|
|

|
Keylogger
What is a keylogger?
A keylogger is something that records keystrokes made on a computer. It captures every key pressed on the keyboard and stores it down in a file or memorybank that can be viewed by the person performing the monitoring in real-time, or at a later date.
What is a keylogger used for?
A keylogger has many uses. Much like a telephone recording system at a call center, the keylogger silently records all keystrokes typed, including emails, word documents, chatroom activity, IRC, instant messages, web addresses and web searching.
Many companies use keyloggers on their company PCs to supervise employees for internet and PC usage compliance. keyloggers can help keep track of activity and allow a company to act on unauthorised activity before it becomes too late.
Here is some sample text recorded with a KeyGhost keylogger
|
<PWR><ctrl-alt-del>Administrator<tab>fabelj68<ent> <PWR><ctrl-alt-del>James<tab>tinna12<ent> <lft><lft><pgu><ent> adrian.cambell@hotmail.com <ent>I'm uploading the design files to the public web server now, could you get them for me? Its the one we used last time but I changed the password to atlanta69. I hope they don't have a keylogger installed. <ent>mike.dobson@jameco.com<ent>Hi, I calculated the sales figures that are projected for the next year. I have put them up on our web server, under http://www.jamecop.com/nonpublic/sales.htm. <PWR><ctrl-alt-del>Administrator<tab>fabelj68<ent>
<ent><lft> davidcoy@jameco.com <ent>Hey, one more
thing, <bks>I got hold of some more files for the design team,
I put them up on the web server under <PWR><ctrl-alt-del>Maco<tab>fisher95<ent><ent>www.hotmail.com |
Interpreting the raw log of recorded keystrokes
If you carefully
read the sample text above, you can get a good idea of the activity of
the first user.
You can tell that the user powered on the PC from the <PWR> command,
then used Control+Alt+Delete combination to log into the Windows NT based
PC as administrator. The Administrator password that is being used becomes
clear as 'fabelj68', and you can see the first website visited is www.yahoo.com
and the second is www.badbarbie.com.
The second time a user ('James') logged into the machine and entered his email program where he typed an email address 'adrian.cambell@hotmail.com' and sent a mail to him outlining his plans to upload the design files from the company PC to a public web server. He includes the password 'atlanta69' in the email, which is the one used to access the web server.
Reading down the log further, you can see the web address of the web server when it is typed into an email to 'davidcoy@jameco.com' the user then powers off and the next user 'Maco' logs in and visits hotmail.com where he logs in as 'Maco3421' with the password 'sdur54' he then checks his email before visiting the website www.l0pht.com, a site that offers a password auditing and recovery application 'L0phtCrack'.
Why use a keylogger?
It is much easier to intercept important information before, or as soon as, it enters the computer system. This is because some keystrokes are immediately hidden or encrypted, such as Hotmail passwords, Yahoo passwords and windows login passwords. The strength of PGP (pretty good privacy) encryption is also another reason to catch keystrokes before they are encrypted by the system, because an intercepted email that has been encrypted with PGP can take many thousands of years to decrypt and read if you don't have the private decryption key.
What different types of keylogger exist?
Essentially there are 2 different types of keylogger, each with their own unique benefits. The comparison is below so you can learn to choose which is the most appropriate for your situation.
1) Software keyloggers

Software keyloggers
are programs that run in the background of a PC and (in most cases) quietly
record every keystroke that is pressed into a file that is stored on the
hard drive.
Some software keyloggers have an added feature to email the recorded keystrokes
to a pre-specified email box where they can be read. This can cause an
increased risk of detection if the user has installed a software firewall
such as 'ZoneAlarm' as it will notify the user of the keylogger transmitting
file causing the suspicious activity.
Other software keyloggers can also monitor incoming and outgoing internet
traffic and perform screen captures, but this tends to slow down even
the fastest PC to a level that could be noticed. Screen capture software
can also quickly fill the hard drive space and cause system stability
problems.
Software keyloggers
can be broken down into 2 sub-categories.
a) Visible in the task manager
b) Invisible and stealth keyloggers
Keyloggers that are visible in the Task Manager can be easily disabled under Windows 95,98, NT, 2000 and XP. It is simply a matter of entering the task manager (Press Control+Alt+Delete and then click on Task Manager) then select the offending keylogger in the applications window and click on the 'End Process' button.
Keyloggers that are invisible and stealth can also be detected and disabled. Some still appear in the Task Manager, but as System Processes under the 'Processes' tab. These can be stopped if the user has sufficient access privileges. Another alternative method is to use a freely available spyware scanning program like Spycop or Adaware. These programs can quickly pick up almost all available software monitoring products with the click of a button. They also feature a database update facility that keeps the scanners up-to-date with detecting the latest releases of the popular monitoring products.
One thing to note
about ALL software keyloggers is that the captured keystroke information
is stored on the PC hard drive where it can be modified, copied off onto
disk, or even via an intruder accessing the PC from the internet.
One way to lower the risk of sensitive data being accessed by the wrong
people is to use a hardware keylogger.
2) Hardware keyloggers
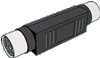
Using a hardware keylogger to record keystrokes is as simple as plugging it in between the keyboard and PC. This can take anyone with little or no experience under 5 seconds to learn and do.
Once a hardware keylogger is connected, it begins recording every keystroke that passes through it into its own internal memory.
No software is needed to record keystrokes with KeyGhost keylogger.
|
BEFORE
|
AFTER
|
 |
 |
|
For security reasons, the photo (above right) is only a representation of what the KeyGhost looks like. The actual KeyGhost is injection moulded to look exactly like an EMC Balun. |
|
The KeyGhost is a completely self contained hardware unit that simply plugs into the keyboard line of any PC. One can record and retrieve keystrokes without ever installing any software on the PC.
The most obvious and main benefit of a hardware based keylogger is that it is completely undetectable using software and spyware scanners. This means they are the keylogger of choice for long term and stealth surveillance applications.
Hardware keyloggers are also a safe option to use if the PC to be monitored is connected to the internet as they store the (sometimes highly sensitive) recorded information in their own internal memory chip that can not be accessed remotely or copied to a disk. Physical access to the keylogger device is required to retrieve the stored keystrokes.
Hardware keyloggers
can also be separate into 2 categories
a) Unsecured onboard memory
b) Encrypted (secured) onboard memory
Essentially these
sub-categories are similar to the software keyloggers.
If a hardware keylogger does not encrypt its memory, then the contents
are available to be read by anyone that has access to the device EVEN
if they don't have the current access password.
When a hardware keylogger uses a STRONG encryption on its memory, then
it becomes virtually impossible for anyone to access the keystrokes that
are secured inside the memory chip if they do not know the password that
was used to encrypt them.
Hardware keyloggers can also be fitted internally inside a keyboard where they are impossible to detect unless the user physically opens up the keyboard and knows where to look.
A hardware keylogger has its own internal microprocessor which means it operates independently of the operating system and will never slow down or crash the system. Because it stores all the keystroke in its own internal memory, the keystrokes can never be lost even if the target computer crashes, fails or its hard drive is removed and/or destroyed.
How do I compare and choose between many different types of keylogger?
Choosing the right keylogger is not a simple task. You should first decide on the level of security that you will require during the monitoring process.
1. Is the information
that will be captured sensitive in any way?
2. Is the computer that you are monitoring connected to the internet?
3. Will multiple users be accessing the computer?
4. Are you interested in both outgoing and incoming information?
5. Do you require screen capture capability? (caution*)
6. Do you need complete stealth during the operation?
7. Is the monitoring target a Power User or relatively inexperienced with
PCs?
8. Does the PC have USB ports or a floppy drive attached?
9. Is the PC hidden under a desk or up in plain view?
10. Is the PC moved on a regular bases?
11. Do you have administrator access on the PC? (required to install software)
12. Will this be a long term or short term operation?
* Screen capture functionality will slow down the PC significantly which may alert the user as to how they are being monitored and increase risk of detection. If the hard drive runs out of space the PC will become unstable and begin crashing.
Find out about
KeyGhost SX, the hardware keylogger
with built-in high speed download capability.
Read more
>>
security,
computer, keyboard, record, keys Comparison? How do I choose keyloggers
work? How can I use What is the best Compare products. undetetable. What
is it and how does it work?. Comparisons, choose, choosing.
Note: Hotmail, Yahoo, Spycop, Adaware, ZoneAlarm and L0phtCrack are the trademarks of their respective owners and are being used as examples for informational purposes only without intent to infringe.

